- Have any questions? Contact us!
- info@dr-rath-foundation.org
December 2, 2022
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at December 2, 2022
Categories
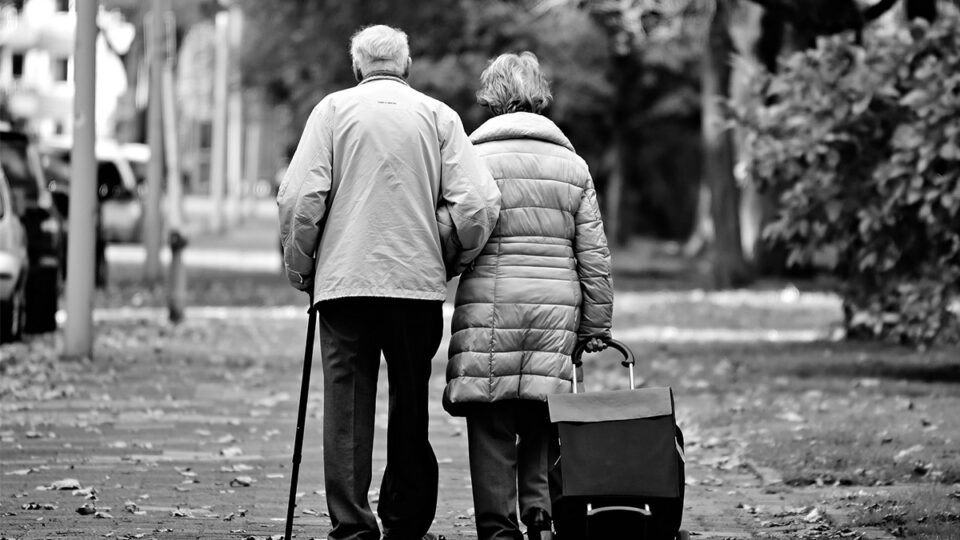
The results of a clinical trial for lecanemab, an experimental drug that is claimed to slow the destruction of the brain in Alzheimer’s disease, have been […]
November 23, 2022
Published by Dr. Rath Health Foundation at November 23, 2022
Categories
October 20, 2022
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at October 20, 2022
Categories
A new systematic review of observational and interventional studies examines the use of antioxidants in patients with COVID-19. Published in the Food Science & Nutrition journal, the results demonstrate highly beneficial roles for this class of micronutrients in reducing inflammation, ventilation requirement, hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, mortality, and other aspects of coronavirus care. Confirming that intravenous supplementation with vitamin C significantly decreases mortality from COVID-19 in severe cases, and that studies show vitamin D, selenium, and zinc similarly play positive roles in fighting the disease, the researchers conclude that antioxidants can improve clinical outcomes.
September 23, 2022
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at September 23, 2022
Categories
In his classic nineteenth century novel ‘War and Peace’ Russian writer Leo Tolstoy observed that “the strongest of all warriors are…time and patience.” I was reminded […]
May 13, 2022
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at May 13, 2022
Categories
In December 2020, as the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic drew towards a close, families across the world were preparing to spend the coming holiday […]
April 29, 2022
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at April 29, 2022
Categories
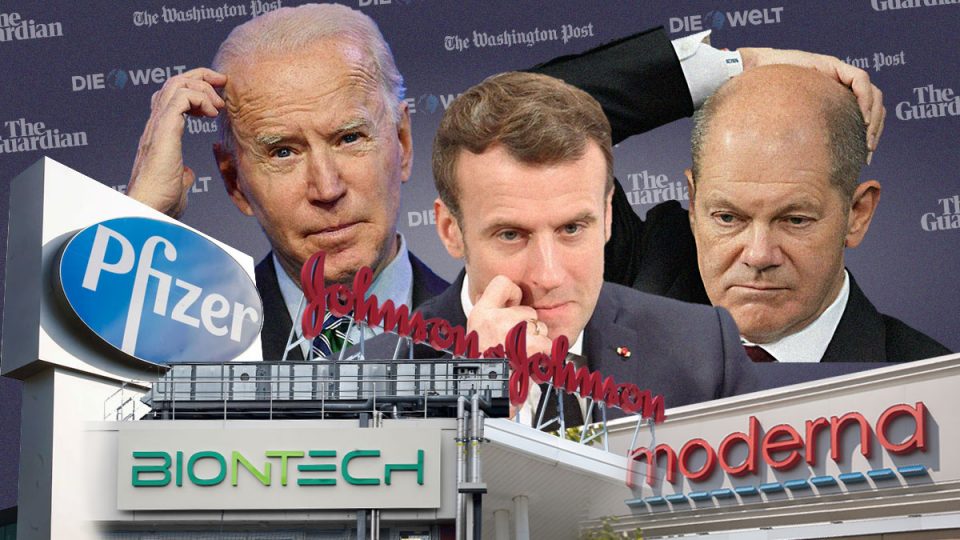
If we were to believe the mainstream media’s spin on the past two years of COVID-19, then the pharma industry saved the world, our governments told […]
May 28, 2021
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at May 28, 2021
Categories
In late April 2020 we published a revealing article describing how Professor Luc Montagnier, the French scientist who shared the 2008 Nobel Prize in Medicine for discovery of […]
November 24, 2016
Published by Paul Anthony Taylor at November 24, 2016
Categories
The Ministry of Peace concerns itself with war, the Ministry of Truth with lies, the Ministry of Love with torture and the Ministry of Plenty with […]